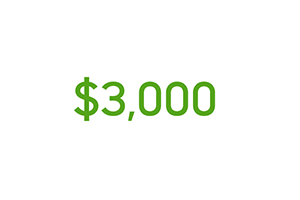Ducted heat pump rebate available for your home. Save up to $800!
Maximize your heating and cooling efficiency and get a heat pump rebate of up to $800 from TVA EnergyRight® and your local power company.
Here’s how our heat pump rebate works:
To help make sure the job’s done right, all TVA EnergyRight rebate-eligible upgrades must be completed by a member of the Quality Contractor Network. Use our “find a contractor” search tool to take the guesswork out of finding a vetted, licensed and insured contractor for your heat pump installation.
Pump up your heating and cooling savings with an energy efficient heat pump.
Great for our seven-state Tennessee Valley region, heat pumps use electricity to transfer heat instead of generating heat. During the cooling season, they move the hot air from your home to the outdoors. During the heating season, they extract heat and pump it into your home. Federal tax credits may also be available on eligible heat pumps. Use the ENERGY STAR Rebate Finder to look for rebates and special offers in your area.
Available heat pump rebates.
| Project | Rebate |
|---|---|
Heat pump (air source or dual fuel) – 17 SEER2 or higher | $800 |
Heat pump (air source or dual fuel) – 15 to 16.99 SEER2 | $500 |
Tune-up for existing heat pump or central air conditioning system | $50 |
Duct sealing, repair, insulation, or replacement* | $300 |
*complete duct system must be brought to TVA standards to qualify
What do SEER2 ratings mean?
SEER2 stands for seasonal energy efficiency ratio. It indicates the maximum energy efficiency of your heat pump, mini split or air conditioner. Basically, the higher the SEER2 rating, the more efficient your unit is.
Access all heat pump rebates through the Quality Contractor Network.
TVA-vetted contractors from our Quality Contractor Network* complete all rebate-eligible upgrades, and they’ll even submit your rebate for you!
*All TVA EnergyRight rebate-eligible upgrades must be completed by a member of the Quality Contractor Network.
Get the FAQs about rebates, DIY Home Energy Assessments, the Quality Contractor Network and more!
Have questions about our rebates? Want to see a list of all of our home energy rebate offerings? Need to learn more about financing? Get the answers to all this and more by visiting our Frequently Asked Questions page.
Rebates
Quality Contractor Network
Financing
Additional available heating and cooling rebates.

Looking for more ways to save?
Discover how your home uses — and loses — energy by taking our new and improved DIY Home Energy Assessment. Get your customized report, rebate and credit recommendations, home improvement gift card, and a free energy-saving kit when you complete the free assessment.
Questions about heat pumps and air conditioners? We have the answers to your HVAC questions!
HVAC FAQs
What is a SEER2 rating?
The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, or SEER, measures how much energy is required to operate the cooling system. The higher the SEER, the better the energy efficiency. Since 2023, the Department of Energy uses an updated version of the original SEER rating called SEER2. By law, new air conditioners must meet a minimum SEER rating of 15 or SEER2 rating of 13.8. It’s also recommended that home air conditioners in the Southeast have a minimum SEER of 15 or 14.2 SEER2 due to the region’s increased heat and humidity.
How do I find my HVAC system’s SEER/SEER2 rating?
You can find your HVAC system’s SEER/SEER2 rating a couple of ways. Head to your outdoor unit and look for the yellow Energy Guide label. The rating will be listed there. You can also look for a piece of paper tied to your indoor unit, or if you’re still not having any luck, try looking up the model and serial number (also labeled on the unit) online or by calling the manufacturer.
Consult a TVA-vetted contractor through our Quality Contractor Network to find out the right AC unit for your home and budget.
What SEER2 rating should I get?
The Department of Energy requires that new air conditioners meet a minimum SEER rating of 15 or 13.8 SEER2. It’s also recommended that home air conditioners in the Southeast have a minimum SEER of 15 or 14.2 SEER2 due to the region’s increased heat and humidity.
It’s a good idea to consult with one of our TVA-vetted contractors from the Quality Contractor Network. They can help you determine the right size unit and SEER2 rating for your home and budget.
Is it time to replace my HVAC system?
With proper maintenance, the average lifespan of an HVAC system is between 15 to 20 years. But the energy efficiency of even a decade-old unit will have already considerably decreased. According to the Department of Energy, replacing a 10-year-old unit with a newer and more efficient model could save you 20% to 40% on your cooling costs.
How do I know what size HVAC system my home needs?
One of the most common mistakes homeowners make when replacing their HVAC system is getting something that’s too big for the home. What many homeowners perceive as not enough cool air inside is actually due to too much indoor humidity caused by an oversized AC unit. Make sure that your system is the right size by requesting “a Manual J load calculation” for your home.
Consult a TVA-vetted contractor through our Quality Contractor Network to find out the right AC unit for your home and budget.
What’s the difference between a mini split, an air source heat pump, a dual fuel heat pump and a central air conditioner?
All the different names for heating and cooling options can be confusing, so let’s break down some of the terminology.
A central air conditioner may be the most familiar type of cooling system to you. It’s generally what most people think of when they think of an AC. If you have a central AC system that simply means your home’s air is conditioned, i.e., brought to the temperature you want, in one central location to then be distributed throughout your home through your duct system. Today, there are a wide range of central air conditioners that can help you increase your indoor comfort, air quality, and energy efficiency. Remember though, a central air system is only as good as your home’s duct system. Holes or cracks in your ductwork allow conditioned air to escape and will quickly eat up your energy savings and increase your energy bill over time.
A heat pump is used to control your home’s indoor climate. It uses electricity to move heat from one place to another. So, in the winter, a heat pump pumps heat from outside your home into your home. In the summer, it pumps heat from inside your home out of your home. Heating and cooling your home with a heat pump is much more energy efficient than other central climate control systems that depend on a fuel source.
An air source heat pump is a type of heat pump that moves heat from inside and outside your home to control your home’s indoor temperature. Its technology is based around air temperature and heat transfer.
A mini split is a type of heat pump, only it often works without a ductwork system. (You may hear a mini split referred to as a ductless mini split, but they’re the same thing.) Typically mounted on a wall or the ceiling, a mini split pumps heat from outdoors to indoors in the winter and from indoors to outdoors in warmer temperatures. Mini splits are a great option for homes without a ductwork system and areas of the home where temperature control is challenging. They’re typically more energy efficient because you can avoid losing cool or warm air through leaky ductwork. Plus, mini splits offer flexibility because you can utilize more than one and place them in different locations around your home.
A dual fuel heat pump is a hybrid heat pump that uses electricity to move and/or produce heat with gas as a backup heat source in cold temperatures. (You may also hear it referred to as a dual source heat pump.) Its energy efficiency comes from toggling between the two sources to pump heat in or outside your home based on the temperature outside and your desired temperature inside. The heat pump portion does most of the heavy lifting by pulling heat from indoors outside. However, when temperatures get cold, the furnace portion turns fuel into heat so you can heat your home quickly.
What is a geothermal heat pump?
A geothermal heat pump is an alternative to an air source heat pump. Rather than heating and cooling your home using outside air (what’s known as an air source heat pump), a geothermal heat pump relies on ground temperature, which changes very little, day to day or season to season. A ground heat exchanger exchanges heat with the earth instead of the air.
While more expensive to install than other more conventional heating and cooling methods, you’ll recoup the additional cost within 5 to 10 years of installation through energy bill savings and less required maintenance. Plus, geothermal heat pumps have a lifespan of nearly 25 years (up to 50 or more years for some internal components) and are a much more energy efficient and reliable heating and cooling source.
What is a dual fuel system?
A dual-fuel system combines two different types of heating technologies to condition the air in your home. They use an energy efficient heat pump for electric heating and cooling and a gas furnace for additional heating as needed.
What is an air source heat pump?
According to Energy.gov, an air source heat pump can save you hundreds of dollars in heating costs each year. Here’s how it works: In heating mode, heat energy is extracted from the outdoor air and brought into your home via a compressor circulating refrigerant. A reversing valve changes the direction of refrigerant flow for the cooling season (and for the winter defrost cycle). In warmer months, heat is extracted from the home and rejected outdoors.

Financing available for home energy upgrades.
Affordable, $0 down financing may be available from your local power company for your home energy upgrades.
Resources for all your home energy needs.
Check out these other helpful home energy services.

Energy-saving advice and education

Energy efficiency rebates